Table of Contents
DPC or Damp Proof Course is an important element of a building or structure that restrict vertical movement of moisture from the basement level to upper part of wall through capillary action.
Detailed information about DPC along with its properties and detailed information is discussed below.
What is DPC?
DPC stand for Damp Proof Course. DPC is applied in the base level to protect the structure from the ill effects of moisture and dampness.
To protect walls at different levels DPC is installed at base of all levels. In a building, DPC treatment is given on each floor, before starting brickwork and laying bricks.
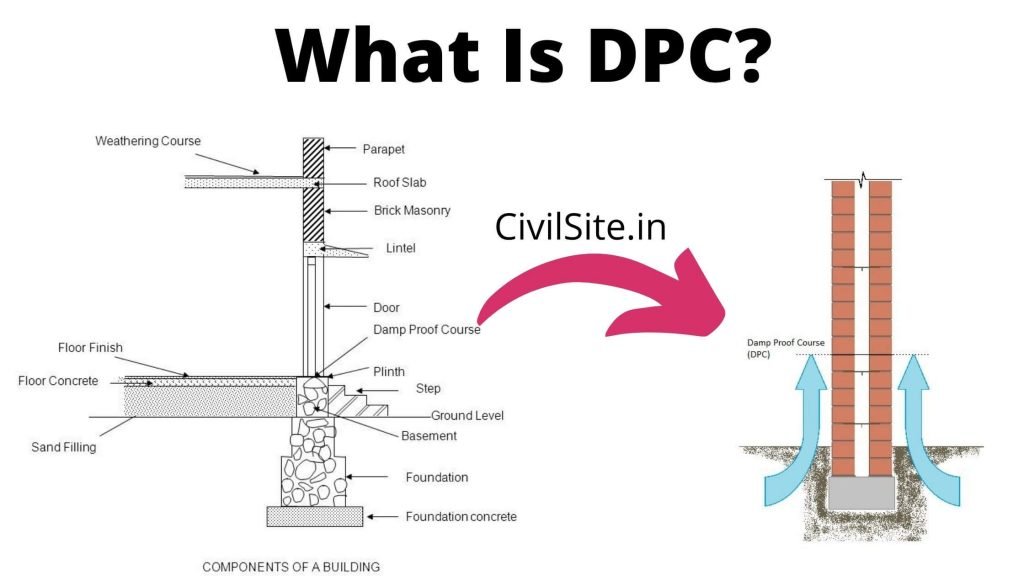
Thus damp proof course helps in preventing water and moisture to damage the walls and interior of home.
DPC Full Form in Different Fields
Let us know fullform of DPC in different fields and its meaning.
DPC Full Form in Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, “DPC” stands for “Damp Proof Course.” A Damp Proof Course is a layer or barrier typically made of materials like bitumen, plastic sheets, or special mortar, which is used to prevent moisture or dampness from rising through walls or floors.
DPC Full Form in Government Services
In the context of government services, “DPC” can stand for “Departmental Promotion Committee.” A Departmental Promotion Committee is a committee formed within government departments or organizations responsible for evaluating and recommending eligible employees for promotions to higher positions within the department.
DPC Full Form in Education
DPC can also stand for a “Diploma in Primary Education,” which is an educational program designed to train individuals to become primary school teachers.
DPC Full Form in Construction
In the context of construction, “DPC” typically stands for “Damp Proof Course.” A Damp Proof Course is a construction technique used to prevent moisture or dampness from rising through walls, floors, or other building components.
DPC Full Form in Promotion
In the context of promotion within organizations or employment, “DPC” can stand for “Departmental Promotion Committee.” A Departmental Promotion Committee is a committee or board typically formed within an organization or government department responsible for evaluating and recommending eligible employees for promotions to higher positions within their respective departments or agencies.
DPC Full Form in Medical
In the medical field, “DPC” can stand for “Direct Primary Care.” Direct Primary Care is a healthcare model in which patients pay a subscription fee directly to their primary care physician or healthcare provider. This subscription fee covers a range of primary care services, such as office visits, preventive care, and basic medical treatments.
DPC Full Form in Railway
- Diesel Power Car: In some railway systems, especially those with diesel locomotives, “DPC” can refer to a “Diesel Power Car.” A Diesel Power Car is a self-propelled rail vehicle that contains a diesel engine to generate power for propulsion.
- Driving Power Car: In the context of high-speed and modern train systems, “DPC” can stand for “Driving Power Car.” A Driving Power Car is typically found at one end of a train and contains the necessary equipment, including the locomotive’s power source, for controlling and propelling the train.
DPC Full Form in Law
In the context of law, “DPC” can stand for “Death Penalty Cases.” This term is used to refer to legal cases or proceedings that involve the consideration of the death penalty as a potential punishment for a serious crime, such as murder.
DPC Full Form in Electricity Bill
In the context of an electricity bill, “DPC” typically stands for “Demand Power Charges.” Demand Power Charges are fees that are applied to a customer’s electricity bill based on their peak electricity usage during a specific billing period.
Causes of Dampness
There are many reasons why dampness in a building can occur. Before beginning with the treatment of dampness and DPC material, let us understand the causes of dampness.
Various causes of dampness are as follows:
- Poor workmanship is one of the main factors of dampness in buildings. Unskilled labour is a prime factor of dampness.
- Vertical movement of groundwater to the wall through capillary action in brick wall.
- Rainwater seeping through outer or external walls
- Structural inappropriateness and faulty construction is also a cause of dampness.
- Inappropriate material selection can also lead to dampness in structure. Poor material selection nowadays accounts for the major reason of dampness.
If proper care and precaution is not taken then dampness can become a nightmare in new building. Thus take note of the above factors and read the precautionary methods of damp proofing course to save your valuable time in redoing work.
Effects of Dampness
Dampness can cause a harmful and severe adverse impact on the structure or building. Some of the effects of dampness in buildings are discussed below:
- Dampness can cause internal and external plaster to peel off and crumble leading to damaged walls.
- One of the main problems of dampness is damaged painting and patches on walls and ceilings. Dampness can lead to flaking and bleaching of paints.
- Dampness can corrode the steel reinforcement and metals used in construction.
- Wooden Furniture like cupboards and beds when in contact with dampness will damage and rot the furniture of your home.
- Dampness can cause short circuits and damage to electrical fittings.
- Termites grow in damp areas caused by dampness thus timber products are in danger of termite attacks.
- Dampness can cause the disintegration of tiles damaged plaster and bricks which can even lead to reduced strength of building.
- Growth of moulds on walls which can cause respiratory allergies.
- Other common problems arising due to dampness are salts, staining, mildew and tide marks.
- Poor performance of insulation is also caused due to dampness or DPC failure.
Suggested for you:
- Standard room sizes and dimensions
- Standard height of plumbing fixtures
- Steel Price Per Kg Today in India 2022
- Standard Door Size
- Standard Size Of Column
Damp Proofing Course Methods
The prime use for a Damp proof course is to stop the ingress of moisture and water up to the walls. There are various methods to do a damp proofing course in a building some of the methods are mentioned below:
- Bituminous membrane damp proofing.
- Integral damp proofing.
- Polyurethane DPC
- Surface treatment.
- Cavity wall construction.
- Guniting.
- Pressure grouting.

Damp Proofing Course Types
Depending on the function and use of damp proofing course, DPC can be listed into three types, which are as follows:
- DPC
- DPM
- Integral Damp Proofing
Let us look in detail at each type of DPC and have brief information about each one. All these types of DPC function to prevent the upward movement of water through capillary action in brickwork or concrete.
- DPC (Damp Proofing Course)
Damp Proofing Course is a layer of waterproofing compound or material applied to stop the ingress of water into the structure. DPC is a layer that intersects the water movement up to the masonry wall as it is usually laid below walls.
2. DPM (Damp Proofing Membrane)
DPM or Damp Proofing Membrane is a membrane of material like Polythene plastic sheet laid onto the probable path of water movement to stop its transmission into the walls.
3. IDP (Integral Damp Proofing)
When waterproofing additives are added directly into to concrete mix to increase its water resistance and make the concrete itself water impermeable then it is termed Integral Damp Proofing.
Difference Between DPC and DPM
As mentioned above DPC is a layer designed to prevent the water from rising into the structure by capillary action by a phenomenon called rising dampness whereas DPM or damp proofing membrane is membrane-like material applied to restrict the movement of moisture.
DPC is a layer of concrete mixture while Damp Proof Membrane (DPM) is a polyethylene sheet underneath the concrete.
Principle For Damp Proof Course
Damp proofing course is important for making the wall damp-proof. But DPC should be done according to the general principle established for damp proof course.
The general principle of the damp proofing course is mentioned below:
- Damp proof course should be continuous and no irregularity or break in layers should be seen.
- DPC can be laid in any direction either horizontally or vertically.
- When damp proofing course is laid horizontally then the thickness of DPC should cover the entire thickness of the wall.
- If damp proofing course is exposed to the external wall surface it can get damaged while doing finishing work.
- Where the horizontal layer of the DPC is continued to the vertical face of the wall then a cement concrete fillet of 75mm radius should be provided at the junction.
- DPC should be continuous, especially at the junction and corners of walls. Otherwise, dampness can get entry from there.
- The supporting mortar bed for damp proof course should be even and leveled and should be free from projection of any sort. This will help DPC to remain intact and safe.
Materials Used for Damp Proof Course
Any material that can inhibit the transmission of water into the structure can be used as DPC material. There are various DPC materials available in the market. Based on the physical and rigidity of the material it can be divided into three types.
Flexible DPC Material
- Hot bitumen
- Plastic sheets
- Bituminous or Asphaltic felts
- Sheets of Leads
Semi-Rigid Material
- Mastic asphalt
- Metal sheets
Rigid Material
- Combination of sheets and felts
- Stones
- Bricks
- Mortar
Properties of DPC Materials
For a material to be used for the Damp Proofing Course it should have following properties:
- DPC material should be impervious.
- Damp proofing material should be dimensionally stable.
- Damp Proof Materials should not contain salt like sulphate nitrate and chloride.
- The material should not be costly and easily available.
- DPC material should be strong enough to bear dead load and live load of a structure or a building.
- Materials used for damp proofing course should be durable.
- It should be flexible so that it can accommodate the structural movements without any fracture.
DPC Thickness
Damp Proofing Course is provided at the base of brickwork to stop water or moisture to seep into walls through capillary action. Normally DPC is provided at the ground level of any structure on which DPC is to be applied.
In building, DPC is usually provided at a height of 400mm maximum upto the level of flooring or top of the plinth.
The thickness of DPC is generally 1.5 inches to 2 inches (40mm – 50mm) if cement mortar is used as DPC mixed with water-resistant admixture and two coats of thin bitumen.
Factors affecting Material Selection of DPC
Damp proof course material should be used according to the application and need. Different materials are suitable for different use. Some of the commonly use DPC material used are shown below:
- A cement concrete ratio of 1:2:4 that is M15 grade of concrete should b used for damp proofing above ground level.
- In humid and damp climatic conditions, higher grades of concrete or rich mix of concrete must be used.
- For better results in DPC water-resistant materials like impermo, waterlock, pudlo can be mixed.
- Flexible materials like bitumen felts, plastic sheets, and mastic asphalt should be used for flooring and roofing.
- DPC material should bond well with the surface.
- In cavity walls, flexible materials like lead strips, and bitumen strips are desired.
Frequently Asked Question
What is full form of DPC?
Full Form of DPC is Damp Proof Course
What is Full form of DPM?
Full Form of DPM is Damp Proofing Membrane
What is DPC in Construction?
To prevent the entry of moisture onto the walls a layer of impermeable concrete or membrane is provided below the brickwall. this layer is called DPC or damp proof course.
What are DPC Materials?
DPC materials are cement mortar mixed with waterproof additives, slate, plastic, metal, special engineered bricks and many more, which you can read above.
Types of Damp Proofing Course?
1. Electro-Osmotic Damp Proof Course.
2. Chemical Damp Proof Course.
3. Pressure Grouting.
4. Membrane Damp Proof Course.
5. Integral Damp Proof Course.
6. Cavity Wall Damp Proof Course.
What is application of DPC?
DPC inhibits the movement of moisture to move upwards through capillary action into walls and floor above.
What are the advantages of Damp Proofing Course?
DPC can prevent damage of paint and plaster and also helps in preventing cracks. DPC increase the shelf life of interior and painting of your home.
Disadvantages of Damp Proofing Course
Normal cracks sometimes develop in this damp proofing process. Also, it provides additional weight to the entire structure. It leads to the level problem. Sometimes it creates ugly patches up to the roof.
How DPC is prepared?
DPC is made of different materials as discussed above. For cement concrete of mix 1:2:4 with a mixture of good-quality waterproofing compound. DPC is 40mm to 50mm thick.
When was DPC invented?
DPC was first invented in 1875
What is difference between DPC and DPM?
DPC is Layer based treatment and DPM is a membrane used for waterproofing.
When was plastic DPC used?
Plastic DPC was used in 1970
Is DPC necessary?
DPC is important to restrict rising damp and avoid water movement through capillary action.
When was damp proof membrane first used?
Damp Proof Membrane was first used in 1960s
What is the DPC level?
Generally DPC level is 150mm above ground level.
What is the thickness of DPC in inches?
The thickness of DPC in inches is usually around 1.5 inches to 2 inches.
What is damp proof course for?
Damp proof course (DPC) is an essential component of the building construction process, which is designed to protect the building from moisture ingress and rising damp. It is a layer of water-resistant material that is usually placed at the base of the walls to prevent water from seeping through.
The primary purpose of DPC is to prevent the ingress of moisture from the ground into the building, which can cause a range of problems such as mould growth, timber decay, and damage to plasterwork and decorations. By creating a barrier to moisture, DPC helps to maintain a healthy indoor environment and protect the structural integrity of the building.
What is the best type of damp proof course (DPC)?
Different types of damp proof course (DPC) are available, including bitumen felt, PVC, and chemical-based solutions. Bitumen felt DPC is an affordable and commonly used option suitable for most construction types. PVC DPC is a more durable and long-lasting option with resistance to chemicals and environmental factors.
Chemical-based DPC involves injecting a chemical solution into the wall to create a moisture barrier and is suitable for situations where physical DPC installation is not possible or treating existing rising damp problems. The choice of the best type of DPC depends on factors like the type of construction, building use, and local environmental conditions and requires the advice of a qualified professional.
2 thoughts on “What is DPC – Damp Proof Course? || DPC Material and Detailed Information”